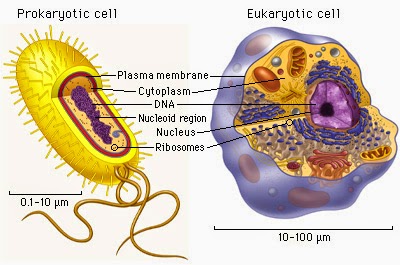
There are two main groups of cells, namely
prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. At prokaryotic cells, genetic material
dispersed within a body like the core that is not surrounded by a membrane.
Eukaryotic cells, have a cell nucleus which is very complex with a core sheath
consisting of two membrane. The following comparison of the differences between
prokaryotic and eukaryotic.
Struktur
|
Prokariotik
|
Eukariotik
|
-
|
+
|
|
Nucleus
|
-
|
+
|
Membrane
nucleus
|
-
|
+
|
-
|
+
|
|
-
|
+
|
|
RNA
|
+
|
+
|
DNA
|
+
|
+
|
-
|
+
|
|
Pigmen
|
+
|
+
|
Histon
|
-
|
+
|
Cells in animals and plants, including eukaryotic
groups. Eukaryotic microorganisms which for instance protozoa, protists and
fungi. There is also a prokaryotic microorganisms, such as bacteria and
blue-green algae.
Cell bacteria and blue-green algae are essentially
the same as plant cells, except for the absence of chloroplasts, nucleus, and
mitochondria. Chlorophyll is spread in the protoplasm. Nucleus is not visible
because the material inside the nucleus dispersed protoplasm and not covered
membrane.
The structure of plant cells and animal cells
An expert Matthias Schleiden plant anatomy and
animal anatomy expert Theodor Shwan, they found every living thing is composed
by cells. For distinguish the structure of plant cells and animal cells, can
use the leaves of Elodea, Hydrilla, or Vallisneria with observed using a light
microscope.
Part of cells and cell organelles in living things
Cells are building blocks of living organisms. That
living things are composed of cells and has been demonstrated through
microscopic observation made by Schleiden.
Transport through the cell membrane of living beings
Cell membrane or plasma membrane located on the
outside of the cytoplasm. In the cytoplasm there are parts called organelles.
All organelles limited by the membrane. Limiting membrane organelles that have
the same molecular structure of the cell membrane, which is made up of fat and
protein molecules.