Carbohydrates are compounds composed macromolecules that
on the elements C, H, and O. carbohydrates can be divided into three as
follows:
1.
Monosaccharides
Monosaccharide are the simplest
carbohydrates because the molecule consists only of a few atoms C and can not
be described by means of hydrolysis into other carbohydrates. Examples of
monosaccharides are glucose, galactose, and fructose.
2.
Disaccharide
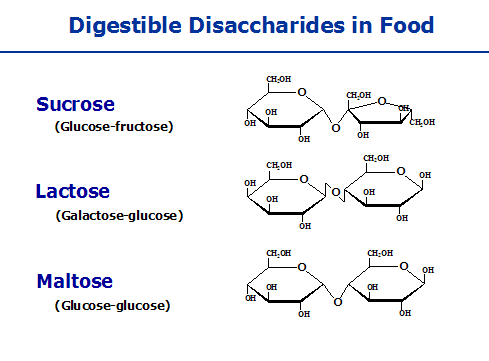
A disaccharide carbohydrate formed from
two monosaccharide molecules bonded through -OH by removing water molecules.
Disaccharides are carbohydrates which when hydrolyzed would produce the same
two monosaccharide molecules or different. Examples are sucrose (cane sugar)
contained in the sugarcane stem cells and lactose (milk sugar) contained in the
milk glands (mammary gland).
3.
Polysaccharides
Polysaccharides are natural polymers
formed from many saccharides as a monomer. Polysaccharides having molecular
formula (C6H10O5)n. There are two kinds
of polysaccharides are homopolysaccharide and heteropolysaccharide. Homopolysaccharide
formed by the same monosaccharide, while heteropolysaccharides built by a
variety of monosaccharides, amino nitrogen, and sulfur.
Homopolysaccharide example:
- Starch (starch), is the result of photosynthesis
- Glycogen, contained in liver cells and muscle cells
- Inulin, found in certain plant root cells as food reserves
- Lignin, contained in the xylem cells
- Cellulose, found in the cell walls of higher plants and serves as a protective cell.
Heteropolysaccharide example:
- Chitin, found in the skin of arthropods, such as crickets, beetles, and grasshoppers
- Heparin, contained in liver cells, lung cells, and the cell walls of arteries as an anticoagulation agent.



0 Response to "Derivatives of Carbohydrates"
Post a Comment